60 Hz vs 50 Hz: Top 5 Key Differences for Your Complete Electronics
When it comes to electronics, the difference between 60 Hz vs 50 Hz can feel a bit like speaking two different languages. Although these terms might seem technical or insignificant at first glance, they play a crucial role in how our devices function around the world. Whether you’re moving abroad, purchasing new appliances, or simply curious about your gadgets, understanding these frequencies is essential for seamless performance. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of electricity and explore what sets 60 Hz vs 50 Hz!
Understanding the Basics: What is Hz and How Does it Affect Electronics?
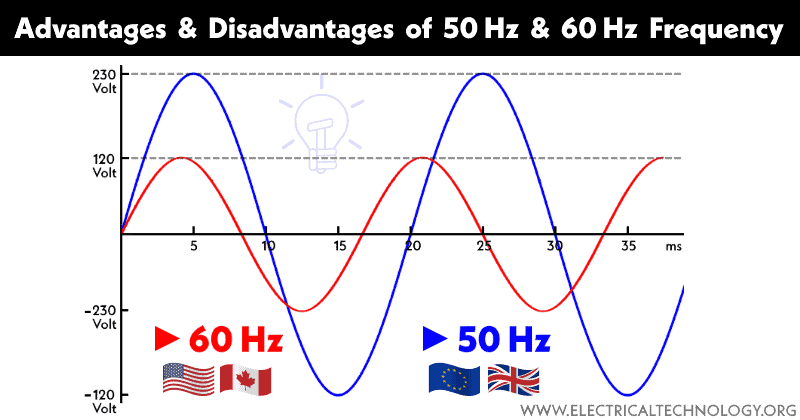
Hertz, often abbreviated as Hz, is a unit of frequency that measures cycles per second. In the context of electricity, it describes how many times an alternating current (AC) changes direction each second.

For instance, in a 60 Hz system, the current changes direction 60 times every second. Conversely, in a 50 Hz system, this occurs only 50 times. This difference might seem minor but can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of electrical devices.
Many home appliances are designed to operate optimally at specific frequencies. When these devices run on their intended frequency, they function smoothly and efficiently. However, using them with mismatched frequencies can lead to issues like overheating or reduced lifespan.
Understanding these basics helps you appreciate why choosing the right frequency matters for your electronics and overall energy consumption.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of 60 Hz vs 50 Hz Frequencies
The debate between 60 Hz vs 50 Hz frequencies brings both pros and cons.
One major advantage of 60 Hz is its efficiency in powering motors. Many electronic devices, particularly those in North America, are optimized for this frequency. This results in smoother performance and better energy consumption.

Conversely, countries using a 50 Hz standard often experience less vibration in their equipment. This can lead to longer lifespan for certain appliances, reducing maintenance costs over time.
On the downside, transitioning from one frequency to another can be tricky. Devices designed specifically for either system may not perform optimally if used interchangeably.
Additionally, there’s an inherent issue with compatibility when traveling or importing electronics across regions with different power systems. It requires careful consideration to avoid potential damage or inefficiency in operation.
Key Differences in Power Systems for 60 Hz vs 50 Hz Countries
The power systems in countries using 60 Hz vs 50 Hz frequency differ significantly. This variance often stems from historical choices made during the early days of electrical engineering.
In 60 Hz regions, like North America, the electrical grid is typically more robust. Higher transmission efficiency at this frequency allows for longer distances without significant energy loss. Devices designed for these systems tend to run slightly faster too.
Conversely, many European and Asian countries operate on a 50 Hz system. While this frequency provides benefits in terms of equipment lifespan and lower heat generation, it may require larger transformers due to increased current at a lower voltage.
These differences affect everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. Understanding these distinctions can be crucial when considering international travel or purchasing electronics abroad.
Compatibility Issues Between Devices with Different Frequencies
When it comes to electrical devices, frequency compatibility can be a significant hurdle. Devices designed for 60 Hz may not operate correctly on a 50 Hz supply and vice versa. This discrepancy often leads to malfunction or damage.
Motors are particularly sensitive to this issue. A device operating at the wrong frequency might overheat, resulting in reduced lifespan or complete failure. Appliances like refrigerators and washing machines could also face inefficiencies, affecting performance.
Transformers and power adapters must match the local grid’s frequency as well. Using an incompatible adapter can lead to inadequate power supply or even short circuits.
Always check your device specifications before plugging in abroad. Being informed helps prevent unnecessary costs from replacements or repairs later on. Understanding these compatibility issues is essential for anyone traveling with electronics across regions with different frequencies.
Tips for Choosing the Right Devices for Your Frequency Needs
When selecting devices, first check the frequency specifications. Look for products designed for your local power supply—60 Hz vs 50 Hz.
Consider voltage compatibility as well. Some appliances operate on a specific voltage range that corresponds with their frequency.
Next, think about adaptability. Many electronics come with built-in converters to handle different frequencies and voltages efficiently.
Research brands that cater specifically to your region’s requirements. This often ensures better performance and reduces potential issues.
Read reviews from users who have similar needs. Their experiences can provide valuable insights into how well a device performs at either frequency level.
By gathering this information, you’ll make informed choices when investing in new electronics tailored to your environment’s needs.
Real-life Examples of the Impact of 60 Hz vs 50 Hz on Electronics
The frequency of electrical systems can have surprising effects on everyday electronics. For instance, many countries operate on 50 Hz, including most of Europe and Asia. This means that appliances designed for these regions often run differently than those built for the 60 Hz standard found in the United States.
Consider a kitchen blender. If you plug a 60 Hz vs 50 Hz outlet, it may not perform as expected. The motor could struggle or even overheat due to insufficient power supply.
Televisions offer another clear example. A TV optimized for 50 Hz might display flickering images when used with a higher-frequency system, leading to an unsatisfactory viewing experience.
Even sound systems aren’t immune; audio quality can suffer when mismatched frequencies interfere with speaker performance. These distinctions highlight how vital understanding frequency is before purchasing new electronics or traveling abroad.
Conclusion: Which one is 60 Hz vs 50 Hz
When it comes to the debate of 60 Hz vs 50 Hz, understanding their differences is crucial for anyone investing in electronics. The choice between these two frequencies often depends on where you live and the compatibility of your devices.
If you’re in a region that typically uses 60 Hz, like North America, most appliances and electronic devices are designed with this frequency in mind. Conversely, countries using 50 Hz tend to have a different set of standards influencing everything from voltage levels to safety regulations.
The advantages or disadvantages associated with each frequency can impact efficiency and performance as well. For example, some motors may run better at one frequency over another. Compatibility issues also arise when bringing devices across borders; not all gadgets handle the switch seamlessly.
For those looking to purchase new equipment or relocate their existing ones internationally, being aware of your specific needs is key—whether it’s checking labels for compatibility or consulting manufacturers about potential adjustments needed for varied frequencies.
Knowing whether you’ll be dealing with 60 Hz vs 50 Hz can save you time and prevent unnecessary frustration down the line. Understanding these distinctions empowers consumers to make informed choices tailored to their unique circumstances.